TensorFlow 2.0 Tutorial 05: Distributed Training across Multiple Nodes

Distributed training allows scaling up deep learning task so bigger models can be learned or training can be conducted at a faster pace. In a previous tutorial, we discussed how to use MirroredStrategy to achieve multi-GPU training within a single node (physical machine). In this tutorial, we will explain how to do distributed training across multiple nodes. This tutorial includes:
- Code boilerplate for multi-node distributed training.
- Example code runs multiple machines.
To reproduce this tutorial, please refer to this distributed training with TensorFlow 2 github repository.
Code Boilerplate
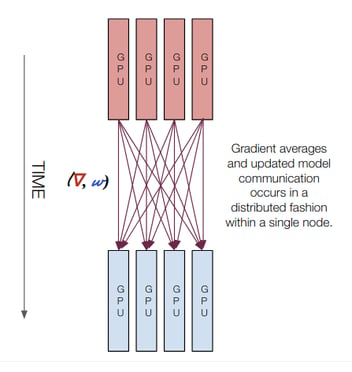
Similar to multi-GPU training within a single node, multi-node training also uses a distributed strategy. In this case, tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy. Multi-node training further requires a TF_CONFIG environment variable to be set. Note that the environment variable will be slightly different on each node. For example, this is the setting on worker 0 in a two-node distributed training job:
os.environ["TF_CONFIG"] = json.dumps({
'cluster': {
'worker': ["10.1.10.58:12345", "10.1.10.250:12345"]
},
'task': {'type': 'worker', 'index': 0}
})
Essentially, TF_CONFIG is a JSON string that represents the cluster and identifies this machine's role in that cluster. The code above sets the TF_CONFIG environment variable which can also be set using a command line export or as a prefix on your shell command for example:
or
TF_CONFIG='{"cluster": {"worker": ["10.1.10.58:12345", "10.1.10.250:12345"]}, "task": {"index": 0, "type": "worker"}}' python worker.py
The cluster field is the same across all nodes. It describes how the cluster is set up. In this case, our cluster only has two worker nodes, whose IP:port information is listed in the worker array. The task field varies from node to node. It specifies the type and index of the node, which is then used to fetch details from the cluster field and given to the task manager to divvy up the work. In this case, this config file indicates the training job runs on worker 0, which is "10.1.10.58:12345"
We need to customize this python snippet for each node. So the second node will have 'task': {'type': 'worker', 'index': 1}.
We then need to create the distributed strategy:
strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy()
Notice this line has to be done after the definition of TF_CONFIG and before the definition of data pipeline and model. Otherwise, a Collective ops must be configured at program startup error will be triggered.
Last bit of the code boilplate defines the model under the strategy scope:
with strategy.scope():
model = resnet.resnet56(img_input=img_input, classes=NUM_CLASSES)
model.compile(
optimizer=opt,
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
model.fit(train_dataset,
epochs=NUM_EPOCHS)
Run the training
To run distributed training, the training script needs to be customized and copied to all nodes. To make it clearer, we can set the environment variable using the prefix syntax. This is set differently on each node.
Make sure the nodes can ssh into each other without the request of the password. The most convenient way to do this is to use ssh keys instead of password authentication. How to use ssh keys.
Last but not least, run the script simultaneously on both nodes.
# On the first node
TF_CONFIG='{"cluster": {"worker": ["10.1.10.58:12345", "10.1.10.250:12345"]}, "task": {"index": 0, "type": "worker"}}' python worker.py
# On the second node
TF_CONFIG='{"cluster": {"worker": ["10.1.10.58:12345", "10.1.10.250:12345"]}, "task": {"index": 1, "type": "worker"}}' python worker.py
The training is now distributed across multiple nodes. The output of the two nodes are synchronized since the Mirrored strategy is used.
Summary
This tutorial explains how to do distributed training in TensorFlow 2. The key is to set up the TF_CONFIG environment variable and use the MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy to scope the model definition.
In this tutorial, we need to run the training script manually on each node with custimized TF_CONFIG. One can see that setting the environment variable quickly become tedious when the number of nodes increases. There are more advanced ways to deploy a distributed training job across a large number of nodes, for example, Horovod, Kubernetes with TF-flow, OpenMPI, or using deployment scripts like Ansible. We will have another tutorial dedicated to that topic.
To reproduce results in this tutorial, please refer to this TensorFlow 2 distributed training tutorial github repository.