Deep Learning Hardware Deep Dive – RTX 3090, RTX 3080, and RTX 3070

Lambda just launched its RTX 3090, RTX 3080, and RTX 3070 deep learning workstation. If you're thinking of building your own 30XX workstation, read on. In this post, we discuss the size, power, cooling, and performance of these new GPUs. But first, we'll answer the most common question:
How many RTX 30XX GPUs can I put in my workstation?
Your workstation should not exceed:
- 2x RTX 3090 – 3x is likely possible with liquid cooling/PCIe extendors*; 4x is not recommended because it would require two PSUs plugged into separate circuits or retrofitting your electrical setup.
- 2x RTX 3080 – 3x will likely require liquid cooling/PCIe extendors* to avoid throttling; 4x is not recommended because it would require two PSUs plugged into separate circuits or retrofitting your electrical setup.
- 4x RTX 3070 – this may require blower edition cards.
* PCIe extendors introduce structural problems and shouldn't be used if you plan on moving (especially shipping) the workstation.
How big are these GPUs?
- RTX 3090 – 3x PCIe slots, 313mm long
- RTX 3080 – 2x PCIe slots*, 266mm long
- RTX 3070 – 2x PCIe slots*, 242mm long
The RTX 3090’s dimensions are quite unorthodox: it occupies 3 PCIe slots and its length will prevent it from fitting into many PC cases. The RTX 3070 and RTX 3080 are of standard size, similar to the RTX 2080 Ti.
* OEMs like PNY, ASUS, GIGABYTE, and EVGA will release their own 30XX series GPU models. Several upcoming RTX 3080 and RTX 3070 models will occupy 2.7 PCIe slots.
How much power do these GPUs use?
The 3000 series GPUs consume far more power than previous generations:
- RTX 3090 – 350W (40% more than RTX 2080 Ti)
- RTX 3080 – 320W (28% more than RTX 2080 Ti)
- RTX 3070 – 220W (88% of the RTX 2080 Ti)
For reference, the RTX 2080 Ti consumes 250W.
These GPUs may overload your circuit (or blow your PSU)
Your workstation's power draw must not exceed the capacity of its PSU or the circuit it’s plugged into.
Circuit limitations
- US home/office outlets (NEMA 5-15R) typically supply up to 15 amps at 120V.
- National Electrical Code states that circuit load should not exceed 80%.
- (1), (2), together imply that US home/office circuit loads should not exceed 1440W = 15 amps * 120 volts * 0.8 de-rating factor.
The above analysis suggest the following limits:
- 3x RTX 3090 per outlet
- 3x RTX 3080 per outlet
- 5x RTX 3070 per outlet (though no PC mobo with PCIe 4.0 can fit more than 4x)
As an example, let’s see why a workstation with four RTX 3090s and a high end processor is impractical:
- 4x RTX 3090 = 4 * 350W = 1400W
- 1x Threadripper 3960X = 280W
- 1x motherboard = 80W
The GPUs + CPU + motherboard consume 1760W, far beyond the 1440W circuit limit.
PSU limitations
The highest rated workstation PSU on the market offers at most 1600W at standard home/office voltages. Workstation PSUs beyond this capacity are impractical because they would overload many circuits. Even if your home/office has higher amperage circuits, we recommend against workstations exceeding 1440W. A PSU may have a 1600W rating, but Lambda sees higher rates of PSU failure as workstation power consumption approaches 1500W.
Are there workarounds to home/office power limitations?
Yes, though we don't recommend them:
- Build a PC with two PSUs plugged into two outlets on separate circuits.
- Retrofit your electrical setup to provide 240V, 3-phase power, or a higher amp circuit.
- Move your workstation to a data center with 3-phase (high voltage) power.
Warning: Consult an electrician before modifying your home or office’s electrical setup.
How should I cool my workstation?
Lambda's cooling recommendations for 1x, 2x, 3x, and 4x GPU workstations:
RTX 3090
- 1x – No concerns.
- 2x – Use standard, non-blower GPUs, large case fans, an air shroud, and have an empty channel that's at least 2x PCIe slots wide between the GPUs.
- 3x – Not yet recommended. Liquid cooling may work, but this needs testing.
- 4x – Not practical due to the power constraints discussed above.
RTX 3080
- 1x – No concerns.
- 2x – Use standard, non-blower GPUs, large case fans, an air shroud, and have an empty channel that's at least 2x PCIe slots wide between the GPUs.
- 3x – Not yet recommended. Liquid cooling may work, but this needs testing.
- 4x – Not practical due to the power constraints discussed above.
RTX 3070
- 1x – No concerns.
- 2x/3x – If not using blower edition cards, have an empty channel that's at least 1x PCIe slot wide between GPUs. Use large case fans.
- 4x – May require blower edition cards, but this needs testing.
Blower vs. non-blower (standard) GPUs
Blower cards pull air from inside the chassis and exhaust it out the rear of the case; this contrasts with standard cards that expel hot air into the case. Here's what they look like:
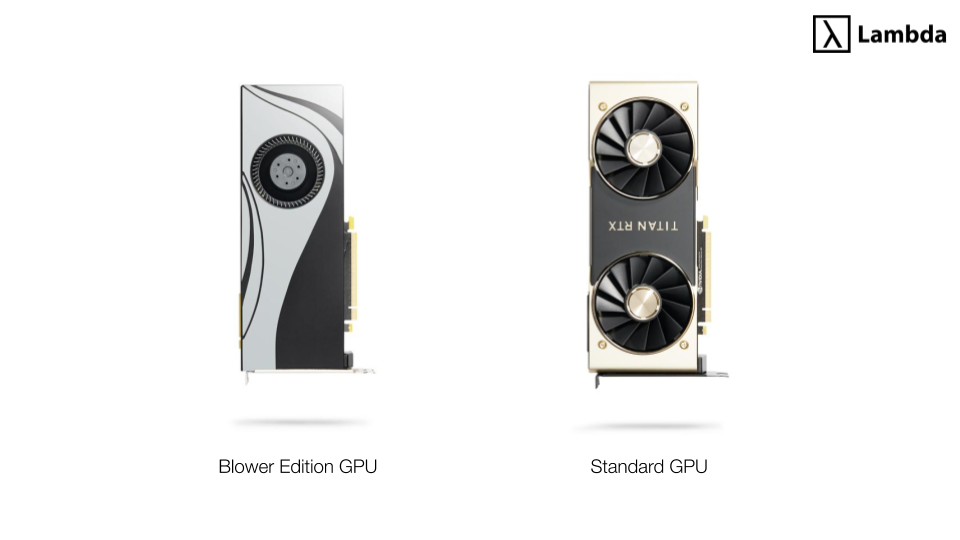

Blower cards are currently facing thermal challenges due to the 3000 series' high power consumption. We fully expect RTX 3070 blower cards, but we're less certain about the RTX 3080 and RTX 3090.
What about liquid cooling?
Liquid cooling will reduce noise and heat levels. It is currently unclear whether liquid cooling is worth the increased cost, complexity, and failure rates. We will be testing liquid cooling in the coming months and update this section accordingly.
Will the GPUs throttle?
When a GPU's temperature exceeds a predefined threshold, it will automatically downclock (throttle) to prevent heat damage. Downclocking manifests as a slowdown of your training throughput. With multi-GPU setups, if cooling isn't properly managed, throttling is a real possibility. Lambda has designed its workstations to avoid throttling, but if you're building your own, it may take quite a bit of trial-and-error before you get the performance you want.
Performance & Cost
The new RTX 3000 series provides a number of improvements that will lead to what we expect to be an extremely impressive jump in performance. It is expected to be even more pronounced on a FLOPs per $ basis.
How well do the new GPUs run my specific deep learning model?
We don’t have 3rd party benchmarks yet (we’ll update this post when we do). However, we do expect to see quite a leap in performance for the RTX 3090 vs the RTX 2080 Ti since it has more than double the number of CUDA cores at just over 10,000! We also expect very nice bumps in performance for the RTX 3080 and even RTX 3070 over the 2080 Ti.
How cost effective are the new GPUs?
On the surface we should expect the RTX 3000 GPUs to be extremely cost effective. Even at $1,499 for the Founders Edition the 3090 delivers with a massive 10496 CUDA cores and 24GB of VRAM. While on the low end we expect the 3070 at only $499 with 5888 CUDA cores and 8 GB of VRAM will deliver comparable deep learning performance to even the previous flagship 2080 Ti for many models. We’ll be updating this section with hard numbers as soon as we have the cards in hand.
How does PCIe Gen 4.0 help?
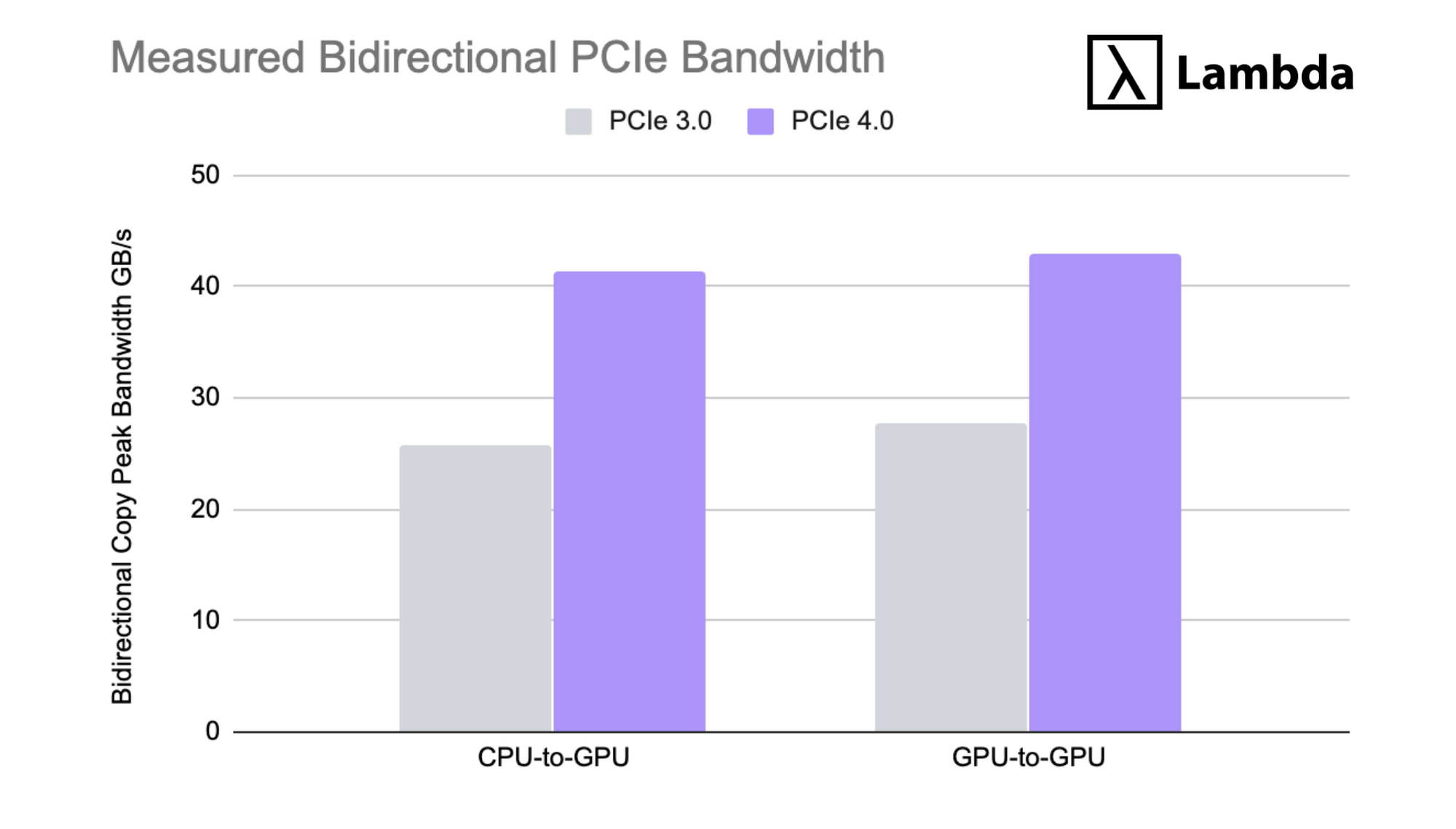
During parallelized deep learning training jobs inter-GPU and GPU-to-CPU bandwidth can become a major bottleneck. PCIe 4.0 doubles the theoretical bidirectional throughput of PCIe 3.0 from 32 GB/s to 64 GB/s and in practice on tests with other PCIe Gen 4.0 cards we see roughly a 54.2% increase in observed throughput from GPU-to-GPU and 60.7% increase in CPU-to-GPU throughput.
Do the new RTX 3000 series GPUs support NVLink?
The RTX 3090 is the only one of the new GPUs to support NVLink. While we don’t have the exact specs yet, if it supports the same number of NVLink connections as the recently announced A100 PCIe GPU you can expect to see 600 GB / s of bidirectional bandwidth vs 64 GB / s for PCIe 4.0 between a pair of 3090s.
However, it’s important to note that while they will have an extremely fast connection between them it does not make the GPUs a single “super GPU.” You will still have to write your models to support multiple GPUs.
Takeaways
It’s important to take into account available space, power, cooling, and relative performance into account when deciding what cards to include in your next deep learning workstation. The biggest issues you will face when building your workstation will be:
- Available PCIe slot space when using the RTX 3090 or 3 slot RTX 3080 variants
- Available power when using the RTX 3090 or RTX 3080 in multi GPU configurations
- Excess heat build up between cards in multi-GPU configurations due to higher TDP
It’s definitely possible build one of these workstations yourself, but if you’d like to avoid the hassle and have it preinstalled with the drivers and frameworks you need to get started we have verified and tested workstations with: up to 2x RTX 3090s, 2x RTX 3080s, or 4x RTX 3070s.